With increasing complexity of wireless local area networks (WLANs), there is a growing need to add more access points while keeping the entire operation simple and easy. Typical access points tend to carry configurations which need to be setup individually. If these get damaged or need replacement, the new access points need to be configured again to match the existing setup. With a frequent need to add or remove access points, a new concept is catching ground in this space – it is called thin access points. Typically, thin access points can perform all the functions of a regular access point but their configuration is controlled by a master switch.
D-Link’s DWL-3500AP is a good example of a thin wireless access point. It has to be deployed in the network in conjunction with DWS-3024 a wireless switch controller with 24 GE ports. The network is termed as Unified Access System and it needs to be deployed as a whole package for the solution to work for the enterprise. However, with a unified solution and a central switch controlling the whole network, the wireless networks tend to perform much better than those created by adding multiple access points in different operation modes.
Wireless Specifications: The D-Link DWL-3500AP is a wireless g thin access point that operates in the 2.4 GHz range. It supports standard throughputs of up to 54 Mbps which can be scaled down in presence of interference to ensure data integrity. The device also supports D-Link’s 108G technology, which can dynamically boost the throughputs up to 108Mbps providing a high bandwidth network for voice and video traffic. The device is also backward compatible with the 802.11b standards allowing older devices to access the network.
As a thin client the two main aspects that matter the most are its coverage area and the ease of installation. With regards to the coverage area, DWL-3500AP comes with a pair of detachable high gain antennas that can be attached and oriented to ensure better coverage and reduced wireless dead spots. The device supports 802.3af or Power over Ethernet standard that allows it to draw power from the Ethernet cable directly rather than rely on a separate power supply. This is vital while installing it in remote places where getting a power outlet may be out of question. The device is connected to the D-Link wireless switch controller which supports PoE on its interfaces; hence the deployment is pretty simple.
Wireless Security: The DWL-3500AP provides 64-bit, 128-bit and 152-bit WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) encryption which ensures a reasonably secured wireless network. However, with WEP keys getting easily hacked, most enterprise deployments have moved to the more advanced WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access) standards. This thin access point can support WPA (Personal and Enterprise) and WPA2 (Personal and Enterprise) versions. With the personal versions, the authentication is done at the access point level itself; this is good for simple SOHO deployments, but risky in the larger WLANs. The Enterprise version works with the 802.1X authentication standard where the initial authentication is done by the enterprise security server. This allows the standard enterprise security to be extended to the WLANs too.
The device also supports Rogue AP detection which prevents unauthorised access points from joining the network. The MAC address filtering helps prevent outside devices from gaining access to the enterprise WLAN. The 802.1Q VLAN tagging feature allows the device to segregate user traffic into distinct VLANs thereby preventing them from mixing with each other. This helps prevent internal intrusions between different set of users. Multiple SSID support enhances the VLAN isolation that the device provides. Besides, with multiple SSIDs, the administrator can rely on a single physical device to create multiple WLANs.
Configuring the Access Point: The best part about a thin client is that it is never configured with any of the network details. It inherits all the configurations from the switch controller at run time. Hence, theft of these access points does not create a risk of sharing enterprise WLAN details. To configure the access point the wireless switch controller needs to be configured first. Follow the steps mentioned below to setup the thin access point.
- Identify the IP address of the switch controller in the network.
- On the computer URL, type in the IP address of the switch controller.
- Enter the username as admin and leave the password field blank.
- This will launch the Basic setup page for the switch.
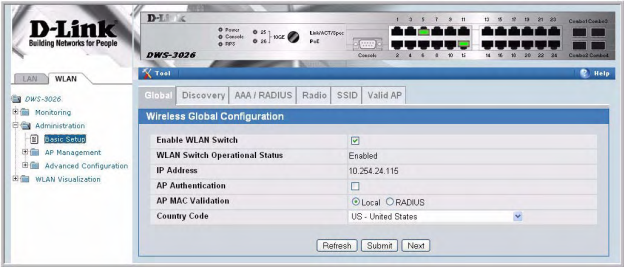
- Configure various parameters for the WLAN(s) on the switch.
- Connect the thin access point to the Gigabit Ethernet port of the switch and power it up.
- The WLAN configuration is automatically downloaded into the thin access point and the wireless network is setup.

